TCFD
Climate Initiatives (reporting based on the TCFD recommendations)
The Enplas Group recognizes climate change as a serious global issue. Through initiatives to reduce our greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and by making continuous improvements in our information disclosure to align with the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), we are working to improve our corporate value.
Climate governance
The Enplas Group recognizes material issues (risks and opportunities) in our response to climate change. We are pursuing sustainable growth by preparing and implementing long-term plans.
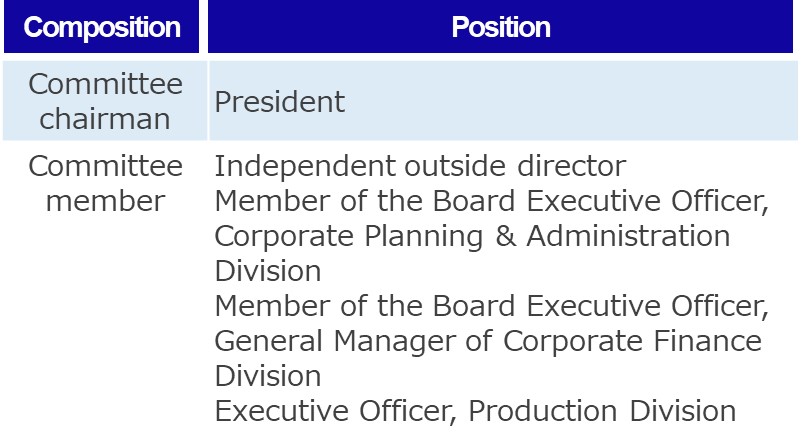
Our Sustainability Committee formulates long-term plans related to material issues (risks and opportunities), including those related to climate change, and manages progress on key goal and performance indicators (KGIs/KPIs), among other activities. The Sustainability Committee is chaired by the Enplas Corporation president and its members consist of directors (including independent outside directors) and executive officers appointed by the chair. Climate measures discussed in the Sustainability Committee are reported to the Board of Directors for further deliberation.
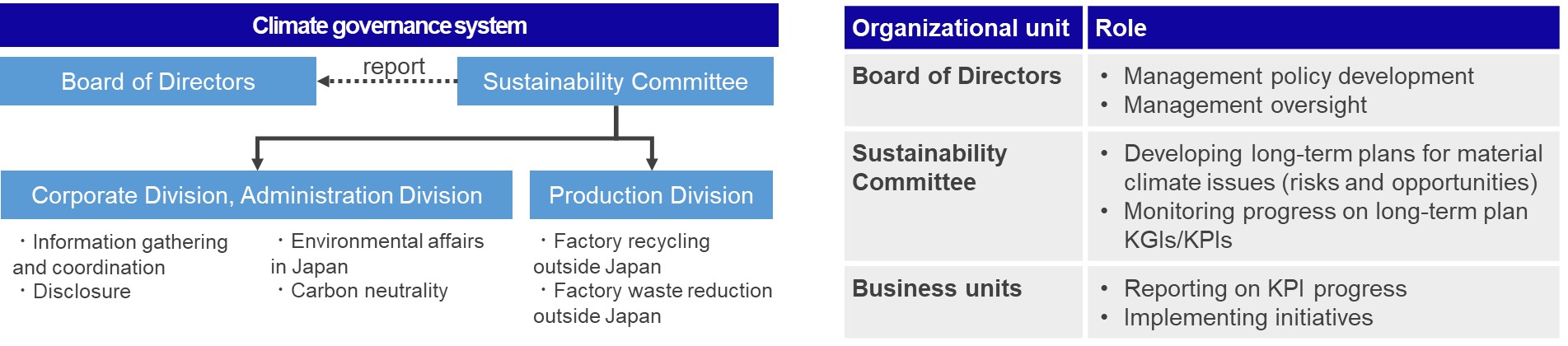
Strategy
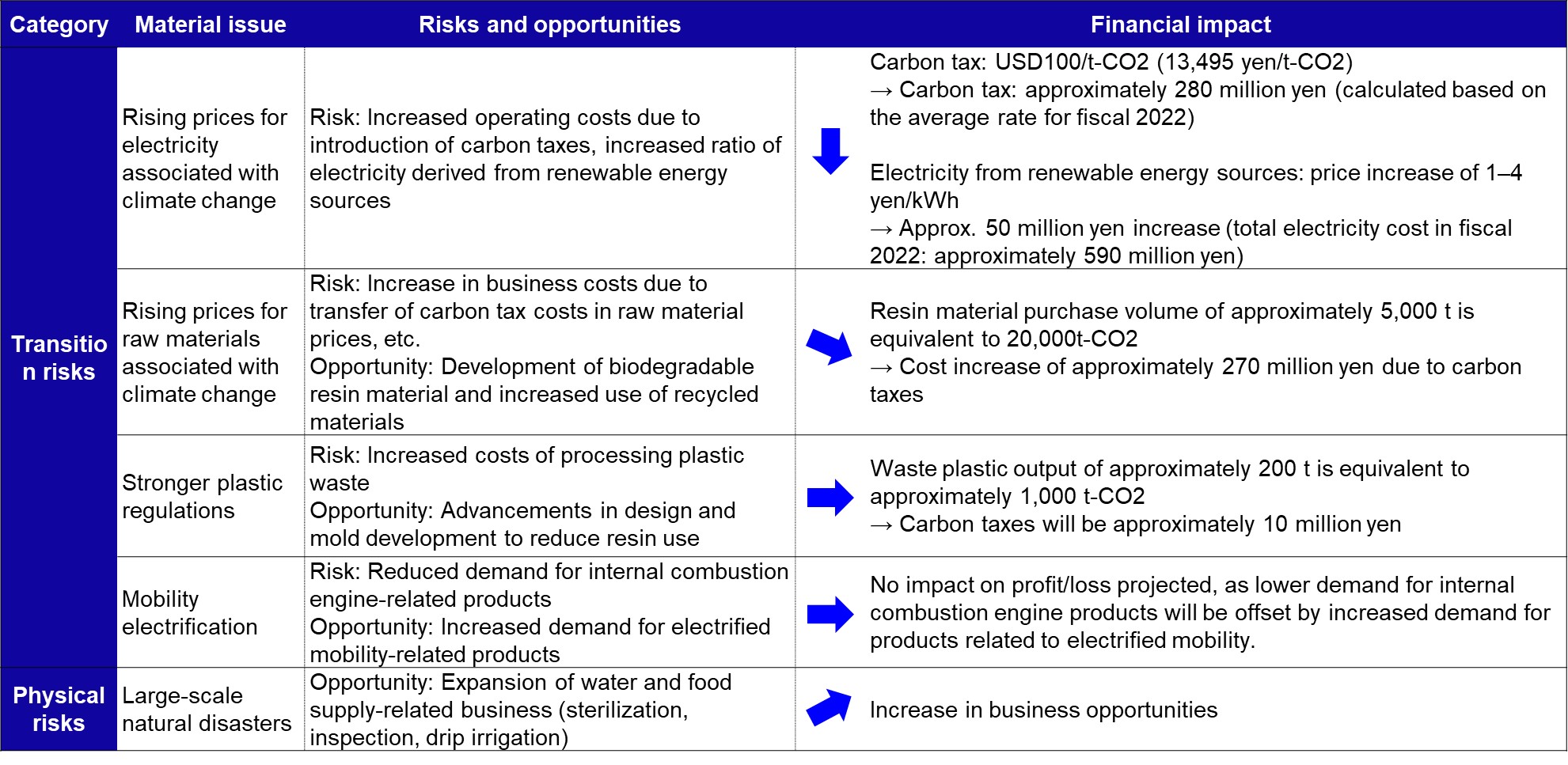
Climate-related risks and opportunities We have identified potential business opportunities and risks associated with future societal challenges such as climate change. In terms of opportunities, we aim to grow our business and enhance our earning power by providing solutions that help address societal challenges in essential business fields that are indispensable to everyday life.
For risks, we anticipate three types of large transition risks associated with climate change: increased operating costs associated with rising raw material and electricity prices, increased costs of processing plastic waste, and reduced demand for internal combustion engine-related products.
| Category | Material issue | Risk | Opportunity | Time frame |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transition risks | Rising prices for raw materials and electricity associated with climate change | Increased operating costs associated with rising raw material and electricity prices | Development of biodegradable resin and increased use of recycled materials | Medium term |
| Stronger plastic regulations | Increased costs of processing plastic waste | Advancements in design and mold development to reduce resin use | Long term | |
| Mobility electrification | Reduced demand for internal combustion engine-related products | Increased demand for electrified mobility-related products | Long term | |
| Physical risks | Large-scale natural disasters | Factory damage caused by extreme weather, especially floods; factory operations stalled by supply chain disruptions | Expansion of water and food supply-related business (sterilization, inspection, drip irrigation) | Long term |
Scenario analysis and impacts of climate-related risks and opportunities on financial planning
■2ºC or lower scenario Climate regulations and policies are strengthened, limiting temperature rise to 2ºC or lower.
Under this scenario, the global price of carbon rises, and governments push for the introduction of a carbon tax. We forecast that the use of electric vehicles (EVs) will increase while the use of gasoline-powered vehicles will decrease, the ratio of renewable energy to total energy demand will increase, and demand for oil will decrease. We assume that transition risk under this scenario will increase, as governments and business partners place stricter demands on companies with large GHG emissions. However, physical risks are estimated to be relatively low, as the intensity of extreme weather events under this scenario will be curbed to a certain extent.
Assumed carbon tax in 2030: 100 USD/tCO2
Renewable energy ratio in 2030: 59%
■4ºC scenario
Climate action is insufficient, and global temperatures rise to approximately 4ºC higher than before the industrial revolution.
Under this scenario, energy demand increases, and oil prices rise. We assume that physical risks, such as increased heavy rainfall and rising sea levels, will increase. However, transition risks are estimated to be low, as carbon taxes will be introduced in only a limited number of countries, and government regulations will not be tightened.
Carbon tax: None
Based on our assumptions for the year 2030, we believe that although our electricity consumption will increase as our business activities expand, our total GHG emissions will remain essentially unchanged as a result of procuring electricity from renewable energy sources and improving our energy efficiency.
In line with the above assumption, we assessed the impact of climate-related risks and opportunities on our financial plan under the 2°C and 4°C scenarios.
For the scenarios used in this analysis, we referenced the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) World Energy Outlook 2021, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s (IPCC) 6th Assessment Report (AR6), and documents published by the Japanese government.
■2ºC or lower scenario
■4ºC or lower scenario

■Impact on Management Strategy
Our analysis of climate change-related risks and opportunities in 2030 indicated that the introduction of carbon taxes and large-scale natural disasters, in particular, would have a significant impact on the Group. We believe that pursuing our top-priority issue of “contributing to essential business fields that enhance QOL for people and the planet” will enable us to increase sales of high value-added products that can provide greater value to our customers and absorb cost increases associated with carbon taxes. In addition, although our customers are spread throughout the world, which enables us to minimize the risk of large-scale natural disasters, our production is primarily located in Japan and Southeast Asia.
■Initiatives in Response to Scenario Analysis
As more than 90% of Enplas Group’s GHG emissions are derived from electricity consumption, we are implementing the following initiatives to reduce our GHG emissions.
・Procurement of electricity derived from renewable sources (installation of solar panels)
・Energy efficiency improvements (replacement of air conditioning systems and other equipment)
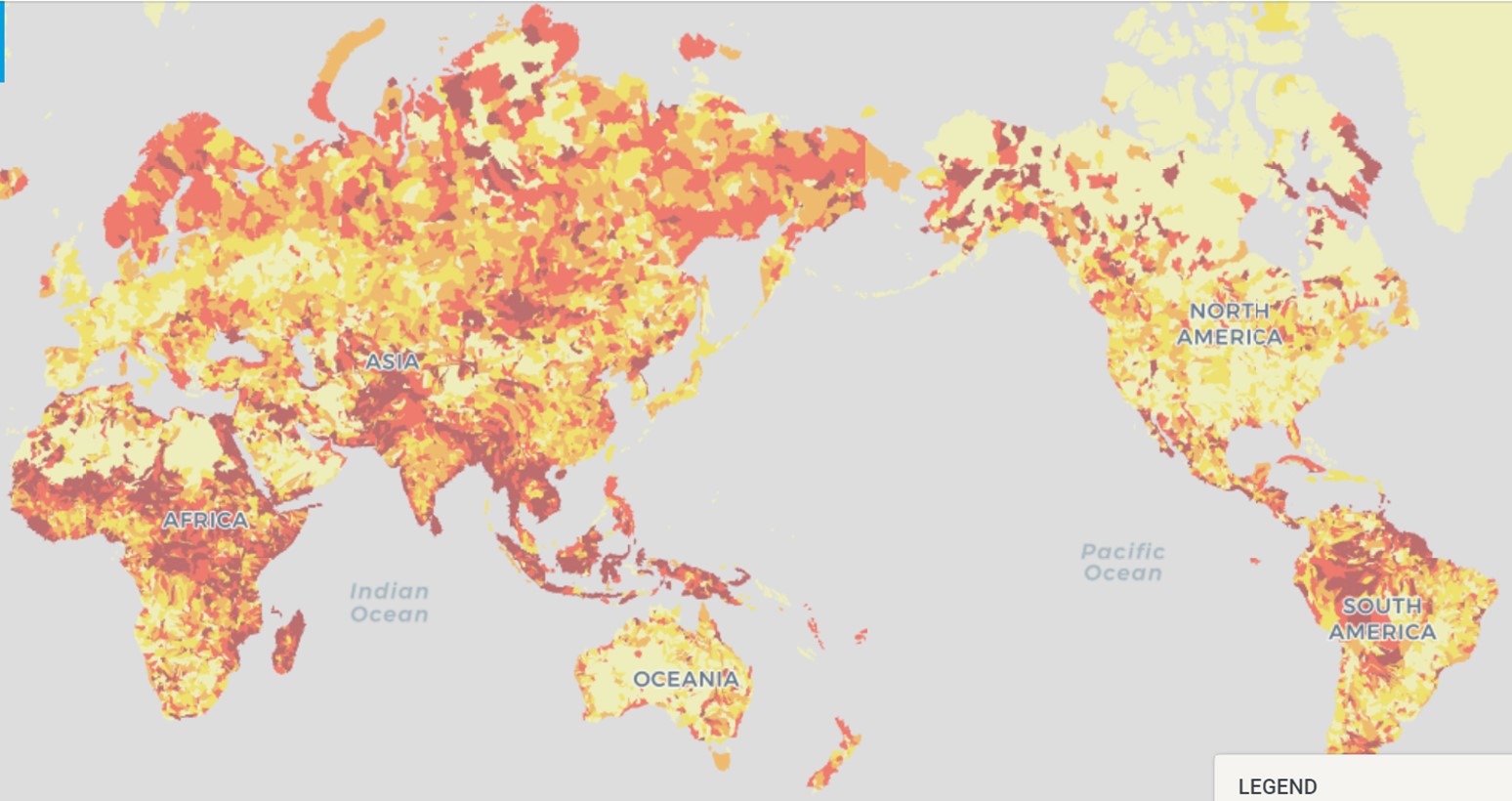
With regard to water risk, we have identified business locations with a high water risk using the WRI Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas tool. Areas with a very high risk of flooding include Vietnam, Indonesia, and Shanghai, while those with a high risk of flooding include the Philippines, Israel, California, and Jiangsu Province (China).
Risk management
We have set in place Regulations for Total Risk Management, which stipulate rules for risk management for the entire Group, and a Total Risk Management Committee tasked with establishing a risk management system under direct control of management. The Total Risk Management Committee works to identify potential future risks relevant to the entire Group, implement measures to prevent such risks, and minimize their impacts when they do occur. Recognizing climate-related risks as a category of risk projected to grow over the medium to long term, we will assess the potential implications of these risks on business strategy and ways to manage them effectively.
For the metrics and targets used to assess climate-related risks and opportunities, please see the ” Metrics and Targets “ page.
Scope 1, 2, and 3 GHG emissions
For Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions data, please see the “Environment (E)” tab. We are currently preparing our Scope 3 data.
- Environment
- Environmental Policy
- Environment
- Social
- R&D
- Compliance
- Human Capital
- Supply Chain
